

Bus Topology is not as fast as Ring Topology.The network performance is at stake and reduces if there are numerous nodes and heavy network traffic.If the main cable collapses, the complete network collapses.Expansion can be done easily by linking the cables together.The working of this topology is easy to understand.The Cable length required is the least in comparison to other topologies.When this topology has precisely two endpoints, it is known as Linear Bus Topology. Data is transmitted in a single route, from one point to the other. every device on the network, is connected to a solo main cable line. If the address doesn't match the node simply regenerates the message and sends it on its way.Bus topology is the kind of network topology where every node, i.e. Message travel around the ring from node to node in a very organized manner.Įach workstation checks the message for a matching destination address.

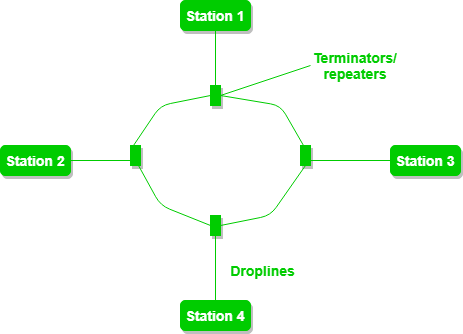
Each device connects directly to the ring or indirectly through and interface device or drop cable. Ring Topology The physical ring Topology is a circular loop of point-to-point links. As a result there is no coordination between the devices for reservation of transmission time slots, so data collisions are frequent. Only one device transmits at a time, other devices wait for their turn.
Network topology in hindi pdf install#
It uses established standards and it is relatively easy to install and the use for small networks.The number of devices and the length of the trunk can be easily expanded.Īdvantages of Bus Topology The advantages of physical bus topology are: This is accomplished using short drop cables or direct T-connectors. All nodes on the bus topology have equal access to the trunk. Bus Network Topology requires a multipoint connection. If the message is missed or not recognized, it reaches the end of the cabling and dissipates at the terminator. Data communication message travels along the bus in both directions until it is picked up by a workstation or server NIC. Without a terminator the electrical signal would reach the end of copper wire and bounce back, causing errors on the network. It consists of one continuous length of cable (trunk) that is shared by all the nodes in the network and a terminating resistor (terminator) at each end that absorbs the signal when it reaches the end of line. Bus Topology The physical Bus Network Topology is the simplest and most widely used of the network designs. They are, Bus Topology, Ring and Star Topology. Basic Network Topology The three simple Topology that are combined to form a basic Network Topology. Primary-Secondary: In this, one device controls the traffic and all other devices transmit through primary device. Peer to Peer: In this relationship, all the devices in the network have equal status in sharing the link.įor example, Ring & Mesh topology. The nodes in a network can have following two relationships: 1.While making a selection of a particular topology we consider the relative status of different devices that are to be linked.Ease of troubleshooting 7.ĭelay involved in routing from one node to another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
